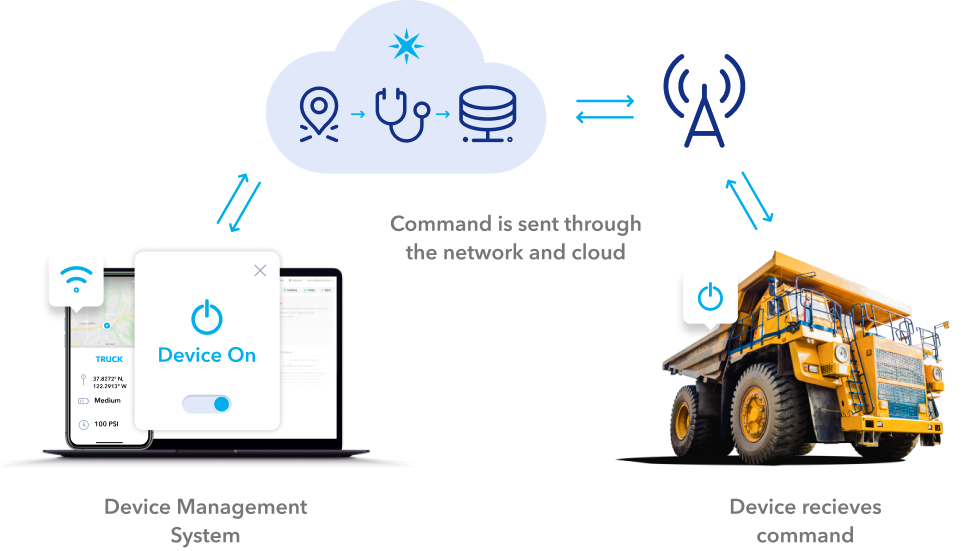
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to revolutionize industries, remote management of IoT examples has become a critical aspect of modern operations. From smart homes to industrial automation, remote management ensures seamless connectivity and control over devices spread across various locations. This article delves into the significance, practical applications, and challenges of remote IoT management, offering actionable insights for businesses and individuals alike.
IoT technology is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a reality shaping our daily lives. Remote management plays a pivotal role in optimizing IoT systems by enabling real-time monitoring, troubleshooting, and updates. This capability not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces costs and improves scalability.
With this guide, you will explore real-world examples, best practices, and expert advice on managing IoT devices remotely. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or an IT professional, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge needed to harness the full potential of IoT remote management.
Read also:Sarah Jeffery Race A Rising Star On The Global Stage
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Remote Management of IoT Examples
- Biography of IoT Technology
- Practical Applications of Remote IoT Management
- Key Benefits of Remote Management in IoT
- Common Challenges in Remote IoT Management
- Effective Solutions for Overcoming Challenges
- Top Tools for Remote IoT Management
- Ensuring Security in Remote IoT Systems
- Scalability Considerations for IoT Networks
- The Future of Remote IoT Management
Introduction to Remote Management of IoT Examples
Remote management of IoT examples refers to the ability to monitor, control, and maintain IoT devices and systems from a distance. This concept leverages advanced communication protocols, cloud computing, and automation to ensure that devices operate optimally regardless of their physical location. The growing adoption of IoT technology across industries has made remote management an essential component of modern infrastructure.
In today's interconnected world, remote management is not just a convenience; it is a necessity. Organizations rely on IoT devices for various functions, from tracking inventory levels in warehouses to monitoring environmental conditions in agriculture. By implementing remote management strategies, businesses can reduce downtime, improve response times, and enhance overall productivity.
Why Remote Management Matters
The importance of remote management lies in its ability to streamline operations and reduce costs. For instance, instead of sending a technician to a remote location to fix a malfunctioning IoT device, administrators can diagnose and resolve issues remotely. This capability not only saves time but also minimizes the need for physical intervention, which is particularly beneficial in hard-to-reach areas.
Biography of IoT Technology
IoT technology has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially conceptualized in the late 1990s, IoT has grown into a global phenomenon with billions of connected devices. Below is a brief overview of its development:
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1999 | Kevin Ashton coins the term "Internet of Things." |
| 2008 | First IoT World Forum held, highlighting the potential of IoT. |
| 2014 | IoT becomes mainstream, with companies investing heavily in IoT solutions. |
| 2023 | Global IoT market valued at over $1 trillion, with remote management playing a crucial role. |
Practical Applications of Remote IoT Management
Remote management of IoT examples finds application in numerous industries. Below are some real-world scenarios where remote IoT management has proven invaluable:
Smart Homes
In smart homes, remote management allows homeowners to control lighting, temperature, and security systems from anywhere in the world. For instance, using a smartphone app, users can adjust the thermostat or check security camera footage remotely.
Read also:Trail Blazer Pining For Kim The Untold Journey
Industrial Automation
Manufacturing plants utilize IoT sensors to monitor machinery performance and predict maintenance needs. Remote management enables engineers to receive alerts and address issues before they escalate, minimizing production disruptions.
Agriculture
Farmers use IoT devices to monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health. Remote management allows them to make data-driven decisions and optimize resource usage, leading to increased yields and reduced costs.
Key Benefits of Remote Management in IoT
Remote management of IoT examples offers several advantages that contribute to its growing popularity:
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for on-site visits and manual interventions.
- Increased Efficiency: Enables real-time monitoring and swift response to issues.
- Enhanced Scalability: Facilitates the management of large-scale IoT networks.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Provides access to accurate, up-to-date information for decision-making.
Common Challenges in Remote IoT Management
Despite its benefits, remote IoT management comes with its own set of challenges:
Data Security
With millions of devices connected to the internet, ensuring data security is a top priority. Cyberattacks targeting IoT devices can compromise sensitive information and disrupt operations.
Network Connectivity
Remote management relies on stable internet connections. Poor connectivity in remote areas can hinder the effectiveness of IoT systems, leading to delays or failures in data transmission.
Device Compatibility
IoT devices from different manufacturers may not always be compatible, making it difficult to integrate them into a unified remote management system.
Effective Solutions for Overcoming Challenges
To address the challenges of remote IoT management, organizations can implement the following strategies:
Encryption and Authentication
Employing robust encryption and authentication protocols can safeguard data and prevent unauthorized access. This ensures that sensitive information remains secure during transmission.
Redundant Connectivity
Implementing redundant connectivity options, such as using both Wi-Fi and cellular networks, can mitigate the risk of connectivity issues in remote areas.
Standardized Protocols
Adopting standardized communication protocols can enhance device compatibility, making it easier to integrate diverse IoT systems into a cohesive remote management framework.
Top Tools for Remote IoT Management
Several tools and platforms are available to facilitate remote IoT management:
IBM Watson IoT
IBM Watson IoT offers advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities to optimize IoT operations. Its user-friendly interface simplifies device management and data visualization.
Microsoft Azure IoT
Microsoft Azure IoT provides a comprehensive suite of tools for building, deploying, and managing IoT solutions. It supports scalable architectures and integrates seamlessly with existing systems.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT
AWS IoT enables secure and reliable communication between devices and the cloud. Its robust infrastructure supports large-scale IoT deployments and offers features like device shadows and rules engine.
Ensuring Security in Remote IoT Systems
Security is a critical consideration in remote IoT management. Organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to protect their systems:
Regular Software Updates
Keeping IoT devices and management software up-to-date is essential for addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring optimal performance.
Access Control
Implementing strict access control policies can prevent unauthorized access to IoT systems. This includes using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls.
Intrusion Detection Systems
Deploying intrusion detection systems can help identify and respond to potential security threats in real-time, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Scalability Considerations for IoT Networks
As IoT networks grow in size and complexity, scalability becomes a key concern. Organizations must plan for future expansion by:
Designing Modular Architectures
Modular architectures allow for easy integration of new devices and systems without disrupting existing operations. This flexibility is crucial for adapting to changing business needs.
Optimizing Resource Allocation
Efficiently allocating resources, such as bandwidth and processing power, can enhance the performance of IoT networks. This involves prioritizing critical functions and optimizing data flows.
Monitoring Network Performance
Continuous monitoring of network performance helps identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. This proactive approach ensures that IoT systems remain scalable and reliable.
The Future of Remote IoT Management
The future of remote IoT management looks promising, with advancements in artificial intelligence, 5G technology, and edge computing driving innovation. These technologies will enable even more sophisticated and efficient remote management solutions, further enhancing the capabilities of IoT systems.
As the IoT ecosystem continues to expand, remote management will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the digital landscape. By staying informed and adopting best practices, organizations can capitalize on the opportunities presented by this rapidly evolving field.
Conclusion
Remote management of IoT examples is a powerful tool that offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, increased efficiency, and enhanced scalability. While challenges such as data security and network connectivity exist, effective solutions are available to overcome these hurdles. By leveraging the right tools and strategies, businesses and individuals can unlock the full potential of IoT technology.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with remote IoT management in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the world of IoT and technology.
References:
- Statista. (2023). Internet of Things (IoT) - Statistics & Facts.
- Gartner. (2022). Top Strategic IoT Trends and Technologies Through 2023.
- IBM. (2023). IBM Watson IoT Platform.